CDL Practice Tests: Logbook Rules
Choose A Section:
Go!What happens after you take 10 consecutive hours either off duty, in the sleeper berth, or a combination of the two?
- Your 14-hour limit will completely reset, but the 11-hour limit will not
- Your 11-hour limit will completely reset, but the 14-hour limit will not
- Your 11-hour and 14-hour limits will completely reset
- Neither the 11-hour nor the 14-hour limits will completely reset
Which of the following is true about getting 10 consecutive hours in the sleeper berth for your 10 hour logbook break?
- All these are true
- You must not interrupt your 10 hour break by going into driving status or on-duty status
- You can combine sleeper berth and off-duty time for your 10 hour break
- Your 11-hour and 14-hour clocks will reset after your 10-hour break
During the 14-consecutive-hour, on-duty period, you can only drive your truck for up to how many total hours?
- 10
- 10.5
- 11
- 14
Which of the following is NOT a legitimate 30-minute break?
- You spend 15 minutes in the sleeper berth and 15 minutes fueling the truck
- You take 15 minutes in the sleeper berth and 15 minutes driving
- You spend 30 minutes counting cargo as the dock workers load it into your trailer
- You take 15 minutes in the sleeper berth and 15 minutes off duty
What do they consider on duty time to be for the logbook?
- All the time you are in the truck or on the dock
- Any time spent in the truck, whether driving or not
- All the time you are working or are required to be ready to work, for any employer.
- All the time you are on the clock for your current employer
What Are The Hours Of Service Regulations?
- Rules that regulate the minimum time drivers must spend resting between driving shifts
- Rules that limit the number of daily and weekly hours you can spend driving and working
- All these are correct
- Rules issued by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), a division within the Department of Transportation
Why must we keep a copy of paper logs on the truck if we're using electronic logs?
- We can run two logbooks to make the use of our time more efficient
- One of the DOT's requirements is that we keep a paper logbook on our truck as a backup if needed.
- All of these are correct
- Paper logs need to be filled out so we can hand dispatch a hard copy of our logbook
If you drive ____ consecutive hours with no breaks, you can not drive a CMV until a 30-minute break is taken:
- 11
- 14
- 8
- 4
You begin your pre-trip inspection at 7:00 am. After that, you drive for only 7 hours with a mix of on-duty time, rest breaks, and driving time. You are not using the split sleeper berth rule. You finish driving at 10:00 pm. Is this legal according to the 11-hour and 14-hour rules?
- No. You can not drive past 9:00 pm according to the 14-hour rule which began at 7:00 am
- Yes, this was legal because you only drove 7 hours out of the 11-hour window
- Yes, this was legal because you finished driving within the 14-hour window
- No. You can not drive past 8 pm according to the 11-hour rule
What is personal conveyance?
- When driving your tractor without the trailer attached
- Moving a commercial motor vehicle after being put out of service by the DOT
- The movement of a commercial motor vehicle for personal use while off-duty
- When a commercial driver is driving his/her own personal vehicle
About The Logbook Rules For Truck Drivers
Truck drivers must use a logbook to record all of their time. The amount of time a driver can spend driving is regulated by the federal government. You must know the logbook rules.
What Are The Hours Of Service Regulations?
HOS regulations are rules issued by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), a division within the Department of Transportation. These regulations limit the number of daily and weekly hours you can spend driving and working. They also regulate the minimum time drivers must spend resting between driving shifts.
Drivers must keep a current log showing all of their working and resting hours. You must keep these logs on an electronic logging device that meets DOT regulations as laid out in the FMCSA guidebook. You can find this information in the ELD rule section 395.22. The ELD rule applies to most motor carriers and drivers currently required to maintain Records Of Duty Status (RODS) per part 395, 49 CFR 395.8 (a). The rule applies to commercial buses, trucks, and Canada and Mexico domiciled drivers.
Why Do Hos Regulations Exist?
The purpose of HOS regulations is to reduce accidents caused by driver fatigue. Many drivers don't like being told when they can and can not drive. Still, studies have proven there are more accidents amongst fatigued drivers. The risk of an accident is directly related to how many hours a driver has been behind the wheel. The DOT designed the HOS regulations to prevent drivers from pushing themselves too hard and to keep carriers from forcing drivers to drive beyond their limits.
The following chart illustrates how driver fatigue increases the likelihood of an accident in a CMV.
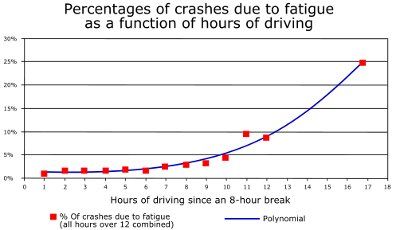
Who Enforces Logbook Regulations?
Generally, DOT officers are the ones who enforce HOS rules, although any police officer may inspect a driver’s electronic logs. Individual states maintain weigh stations where they pull drivers in for random vehicle and logbook inspections. Police officers and DOT officers may also pull drivers over for random vehicle checks and log inspections.
13.3 Determining On-duty And Off-duty Time
Four Types Of Duty Status
There are four types of duty status you can log in your logbook:
- Off Duty
- Sleeper Berth
- On Duty (not driving)
- Driving
The hours of service rules will determine when you can drive based upon the amount of time you have spent either on duty or driving versus sleeper berth or off duty. First, let's talk about on-duty time.
What Is Considered On-duty Time?
The 60 / 70-hour limit is based on how many hours you work over a 7 or 8-day period. Just what kind of work is considered on-duty time? It includes all time you are working or are required to be ready to work for any employer.
Here are some specific activities that are considered to be on-duty time:
- All time spent at a plant, shipping / receiving facility, terminal, or other facility of a motor carrier, unless you are in your sleeper berth or have been relieved of all work-related responsibilities.
- All driving time.
- All time loading, unloading, supervising, or attending your truck; or handling paperwork for shipments.
- All time spent doing any other work for a motor carrier, including giving or receiving training and driving a company car.
- All time inspecting or servicing your truck, including fueling it and washing it.
- All other time in a truck unless you are resting in a sleeper berth.
- All time spent providing a breath, saliva, hair, or urine sample for drug / alcohol testing, including travel to and from the collection site.
- All time spent doing paid work for anyone who is not a motor carrier, such as a part-time job at a local restaurant.
The bottom line is that on-duty time includes:
- All time you are working for a motor carrier, whether paid or not
- All time you are doing paid work for anyone employer.
- All the time you are required to be ready to work for any employer (on-call)
What Is Considered Off-duty Time?
By understanding the definition of on-duty time, you will get a good idea of what they consider off-duty time. For time to be considered off duty, you must be relieved of all responsibility for performing work and be free to pursue activities of your own choosing.
If you are not doing any work (paid or unpaid) for a motor carrier, and you are not doing any paid work for anyone else, you may record the time as off-duty time.
Personal Use Of A Commercial Motor Vehicle
Occasionally, you may use a truck for personal reasons and not for commerce. You may move your personal belongings to a new house or, as a hobby, you may take your horses to a horse show. As long as the activity does not support a business, you are not operating in commerce. If you are not operating your truck in commerce, you are not subject to the hours of service regulations.
Hours Of Service Limitations
HOS regulations determine when and how long you are allowed to drive a commercial motor vehicle (CMV). This is accomplished by placing specific limits on the number of hours you can drive or be considered on duty. The rules also specify how much time you must remain off duty before you can legally resume any driving duties. And finally, the regulations dictate when breaks are required during your workday.
There are three limits and one break requirement which must be followed at all times. They are:
- The 14-hour, on-duty limit
- The 11-hour-driving limit
- The 60/70-hour, on-duty limit
- The 30-minute break
THE 34-HOUR RESTART
The regulations allow you to restart your 60 or 70-hour clock calculations after having at least 34 consecutive hours off duty. In other words, after you have taken at least 34 consecutive hours off duty, you have the full 60 or 70 hours available again.
A driver may take a 34-hour reset at any time, as often as they like. You don’t have to be at home to take a 34-hour break. You can take it on the road. One nice thing about taking a 34-hour break on the road is that it gives you a chance to see something in the area that might interest you. When taking a 34-hour break, you may log it all as off duty, or you can mix in some sleeper berth time if you want. The main thing is that you don’t interrupt your break with any on-duty or drive time.
The 34-hour reset is not a mandatory requirement. It is an option that gives a driver more flexibility in their schedule.
If you choose not to take a 34-hour reset and you're near the limit of your 70 hours, you may find the time you have available each day equals the hours that became available after the 8th day drops off the calculation. They commonly refer to this as “running on re-caps.”




 TT On Facebook
TT On Facebook