Note: Your are not logged in. We can not keep your scores or track your progress unless you Register and Log In
The Securement System
What is a securement system?

A securement system is a securement method that uses one or a combination of the following elements:
- Vehicle Structure.
- Securing Devices.
- Blocking and Bracing Equipment.
What securement system should you choose?
The securement system chosen must be appropriate for the cargo's size, shape, strength, and characteristics.
Are there any requirements for the cargo?
The articles of cargo must have sufficient structural integrity to withstand the forces of loading, securement, and transportation.
This includes packaged articles, unitized articles, and articles stacked one on the other.
Components of a Securement System
Vehicle structure
What is included?
- Floors
- Walls
- Decks
- Tiedown anchor points
- Headboards
- Bulkheads
- Stakes
- Posts
- Anchor points.
Note: Generally, the cab shield is not part of the cargo securement system. However, a front-end structure could be used to provide some restraint against forward movement if the cargo is in contact with it.
How strong must the vehicle structure and anchor points be?
All elements of the vehicle structure and anchor points must be strong enough to withstand the forces described on page 7.
- Forward force: 0.8 g (80%)
- Rearward force: 0.5.g (50%)
- Sideways force: 0.5 g (50%)
- Upward force: 0.2 g (20%)
All elements of the vehicle structure and anchor points must be in good working order:
- No obvious damage.
- No distress.
- No weakened parts.
- No weakened sections.
What is a securing device?
Any device specifically manufactured to attach or secure cargo to a vehicle or trailer:
- Synthetic Webbing
- Chain
- Wire rope
- Manila rope
- Synthetic rope
- Steel strapping
- Clamps and latches
- Blocking
- Front-end structure
- Grab hooks
- Binders
- Shackles
- Winches
- Stake pockets
- D-rings
- Webbing ratchet
- Bracing
- Friction mat
What is a tiedown?
A combination of securing devices that forms an assembly that:
- Attaches cargo to, or restrains cargo on a vehicle.
- Is attached to anchor point(s).
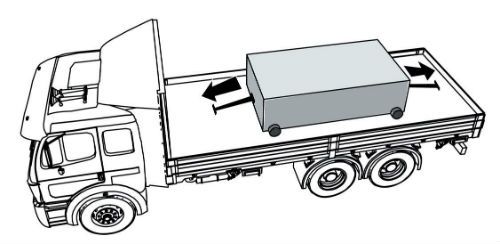
Some tiedowns are attached to the cargo and provide direct resistance to restrain the cargo from movement.
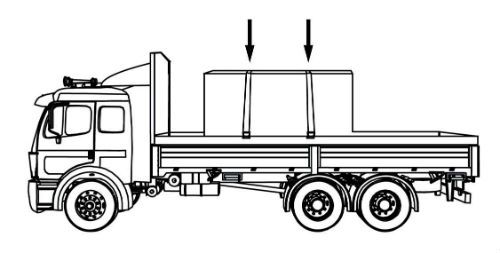
Some tiedowns pass over or through the cargo. They create a downward force that increases the effect of friction between the cargo and the deck. This friction restrains the cargo.
Tiedown construction and maintenance
A tiedown must be designed, constructed, and maintained so that the driver can tighten it (Exception: steel strapping).
All components of a tiedown must be in proper working order.
- No knots or obvious damage
- No distress
- No weakened parts
- No weakened sections
Tiedown use
Each tiedown must be attached and secured so that it does not become loose or unfastened, open, or release during transit.
All tiedowns and other components of a cargo securement system must be located within the rubrails (when present).
Note: This requirement does not apply when the width of the load extends to or beyond the rubrails.
 Related Cargo Securement Terms That Every Driver Should Know:
Related Cargo Securement Terms That Every Driver Should Know:
-
Tiedown:
A combination of securing devices which form an assembly that attaches cargo to, or restrains cargo on, a vehicle or trailer, and is attached to anchor point(s).
-
Contained:
Cargo is contained if it fills a sided vehicle, and every article is in contact with or sufficiently close to a wall or other articles so that it cannot shift or tip if those other articles are also unable to shift or tip.
-
Blocking:
A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against or around an article to prevent horizontal movement of the article.
Multiple-Choice Questions:
Which of the following can be used as part of the cargo securement system?
- Vehicle structure.
- Blocking and bracing equipment.
- All of these are valid.
- Securing devices.
What is a securement system?

A securement system is a securement method that uses one or a combination of the following elements:
- Vehicle Structure.
- Securing Devices.
- Blocking and Bracing Equipment.
How many knots are acceptable in a properly working tiedown?
- 1
- 3
- 2
- 0
All components of a tiedown must be in proper working order.
- No knots or obvious damage
- No distress
- No weakened parts
- No weakened sections
'Blocking' is defined as:
- A vertical barrier across the front of the deck of a vehicle to prevent forward movement of cargo.
- A tapered or wedge-shaped piece used to secure round articles against rolling.
- A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against or around an article to prevent horizontal movement of the article.
- A rail along the side of a vehicle that protects the side of the vehicle from impacts.
Blocking:
A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against or around an article to prevent horizontal movement of the article.
How much force is the securement system required to withstand in terms of cargo weight?
- 50% forward, 50% rearward, 50% sideways, 80% upwards.
- 80% forward, 50% rearward, 50% sideways, 20% upwards.
- 50% forward, 20% rearward, 50% sideways, 20% upwards.
- 80% forward, 50% rearward, 80% sideways, 20% upwards.
How strong must the vehicle structure and anchor points be?
All elements of the vehicle structure and anchor points must be strong enough to withstand the forces described on page 7.
- Forward force: 0.8 g (80%)
- Rearward force: 0.5.g (50%)
- Sideways force: 0.5 g (50%)
- Upward force: 0.2 g (20%)
Cargo is contained when:
- It fills a void between articles of cargo and the structure of the vehicle that has sufficient strength to prevent movement of the articles of cargo.
- It is packed in a square box.
- It is loaded on the end of the truck.
- it fills a sided vehicle, and every article is in contact with or sufficiently close to a wall or other articles so that it cannot shift or tip if those other articles are also unable to shift or tip.
Contained:
Cargo is contained if it fills a sided vehicle, and every article is in contact with or sufficiently close to a wall or other articles so that it cannot shift or tip if those other articles are also unable to shift or tip.
A tiedown is defined as:
- A rail along the side of a vehicle that protects the side of the vehicle from impacts.
- A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against or around an article to prevent horizontal movement of the article.
- A combination of securing devices which form an assembly that attaches cargo to, or restrains cargo on, a vehicle or trailer, and is attached to anchor point(s).
- A strip of material that may be used to unitize articles and is tensioned and clamped or crimped back upon itself. (same as "Strapping")
Tiedown:
A combination of securing devices which form an assembly that attaches cargo to, or restrains cargo on, a vehicle or trailer, and is attached to anchor point(s).
Load securement for cargo weighing 29,650 lbs must be able to withstand upward force of how many lbs?
- 30,000 lbs
- 5,930 lbs
- 29,650 lbs
- 14,825 lbs
How strong must the vehicle structure and anchor points be?
All elements of the vehicle structure and anchor points must be strong enough to withstand the forces described on page 7.
- Forward force: 0.8 g (80%)
- Rearward force: 0.5.g (50%)
- Sideways force: 0.5 g (50%)
- Upward force: 0.2 g (20%)
Complete!
You can Return To The Table Of Contents




 TT On Facebook
TT On Facebook