Note: Your are not logged in. We can not keep your scores or track your progress unless you Register and Log In
Cargo Tie-Downs And Working Load Limit
Tiedowns attached to the cargo
- Tie-downs attached to the cargo work by counteracting the forces acting on the cargo
- The angle where the tie-down attaches to the vehicle should be shallow, not deep (ideally less than 45).
- To counteract forward movement, attach the tie-down so it pulls the cargo toward the rear of the vehicle.
- To counteract rearward movement, attach the tie-down so it pulls the cargo toward the front of the vehicle.
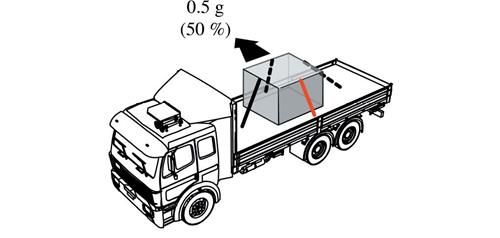
To counteract movement to one side, attach the tie-down so it pulls the cargo toward the opposite side of the vehicle.
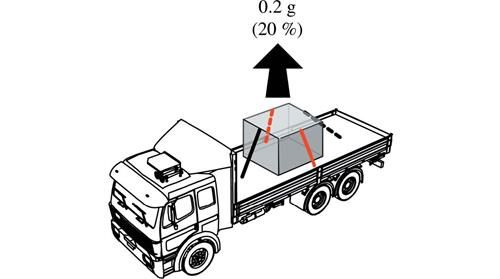
To counteract upward movement, attach tie-downs to opposing sides of the cargo so they pull the cargo down.
Tiedowns that pass over the cargo
Tie-downs that pass over the cargo work by increasing the effective weight of the cargo (make the cargo seem heavier). This increases the pressure of the cargo on the deck and keeps the cargo from shifting.
Tension these tie-downs to as high an initial tension as possible
The steeper the tie-down angle, the less shifting (ideally more than 45).
What should you use in low-friction situations?
When there is low friction between the cargo and the deck (for example, with snow, ice, sand, gravel, and oil):
- Use tie-downs attached to the cargo.
- Use a means to improve the friction such as friction mats or tie-down that pass over the cargo.
- Use blocking and tie-downs.
Containing, Immobilizing, and Securing Cargo: Using Adequate Securing Devices
What is a Working Load Limit (WLL)?

The Working Load Limit is the maximum load that may be applied to a component of a cargo securement system during normal service.
The WLL is usually assigned by the component manufacturer.
WLL for tiedowns.
The WLL for a tie-down is the lowest WLL of any of its parts or the WLL of the anchor points it is attached to, whichever is less. Every device contributes to the WLL of the securement system.
For a synthetic webbing tie-down, the WLL is the working load limit of the tie-down assembly or the anchor point it is attached to, whichever is less.
Note: The minimum WLL requirement for the securement system is 50%. More tie-down capacity should be used if you need to secure an article against any movement.
WLL for blocking systems
The WLL of all components used to block cargo from forward movement must be 50% (or more) of the weight of the article being blocked.
Working Load Limits: marked components
Some manufacturers mark their manufactured securing devices with a numeric WLL value. The WLL for these devices is equal to the numeric value assigned by the manufacturer.
Other manufacturers mark components using a code or symbol that is defined in a recognized standard. For example:
A piece of grade 7 chain may be marked with a 70 or 700, in accordance with the standard of the National Association of Chain Manufacturers. The standard then gives the WLL for that piece of chain, depending on its size.
Working Load limits: unmarked components
Any securing device that is not marked by the manufacturer is considered to have a WLL as specified in Appendix A: Default WLLs for Unmarked Tie-downs.
Carriers are recommended to purchase and use components that are rated and marked by their manufacturer. In that way, the carrier, driver, shipper and inspector can all verify that the proper equipment is being used for the job.
Note: Friction mats, which are not marked by the manufacturer, are assumed to provide resistance to horizontal movement equal to 50% of the cargo weight that is resting on the mat.
 Related Cargo Securement Terms That Every Driver Should Know:
Related Cargo Securement Terms That Every Driver Should Know:
-
Edge protector:
A device placed on the exposed edge of an article to distribute tiedown forces over a larger area of cargo than the tie-down itself, to protect the tie-down and/or cargo from damage, and to allow the tie-down to slide freely when being tensioned.
-
Intermodal Container:
A reusable, transportable enclosure that is especially designed with integral locking devices that secure it to a container chassis trailer to facilitate the efficient and bulk shipping and transfer of goods by, or between various modes of transport, such as highway, rail, sea, and air.
-
Stake Pocket:
A female housing fixed to the side or ends of a vehicle to receive a stake or peg, and may also be used as an anchor point.
Multiple-Choice Questions:
The term 'edge protector' refers to:
- A device placed on the exposed edge of an article to distribute tiedown forces over a larger area of cargo than the tiedown itself, to protect the tie-down and/or cargo from damage, and to allow the tiedown to slide freely when being tensioned.
- A vertical barrier placed directly behind the cab of a tractor to protect the cab in the event cargo should shift forward.
- A rail along the side of a vehicle that protects the side of the vehicle from impacts.
- A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against an article to prevent it from tipping that may also prevent it from shifting.
Edge protector:
A device placed on the exposed edge of an article to distribute tiedown forces over a larger area of cargo than the tiedown itself, to protect the tie-down and/or cargo from damage, and to allow the tiedown to slide freely when being tensioned.
A female housing fixed to the side or ends of a vehicle to receive a stake or peg, and may also be used as an anchor point is a:
- Cleat
- Bulkhead
- Void filler
- Stake pocket
Stake Pocket:
A female housing fixed to the side or ends of a vehicle to receive a stake or peg, and may also be used as an anchor point.
What is the maximum weight that can be secured by a tiedown with a marked WLL of 5,000 lbs?
- 10,000 lbs
- 6,000 lbs
- 2,500 lbs
- 5,000 lbs
Note: The minimum WLL requirement for the securement system is 50%. More tiedown capacity should be used if you need to secure an article against any movement.
Which of the following is not true of Working Load Limit (WLL)?
- The WLL is usually assigned by the component manufacturer.
- The minimum WLL requirement for the securement system is 25%.
- All of these are true.
- The Working Load Limit is the maximum load that may be applied to a component of a cargo securement system.
The Working Load Limit is the maximum load that may be applied to a component of a cargo securement system during normal service.
The WLL is usually assigned by the component manufacturer.
Note: The minimum WLL requirement for the securement system is 50%. More tiedown capacity should be used if you need to secure an article against any movement.
In case of low friction between the cargo and deck, which of these is not a solution?
- Set the cargo on friction mats.
- Put something heavy on top of the cargo.
- Use some kind of blocking.
- Attach tiedowns to the cargo.
What should you use in low-friction situations?
When there is low friction between the cargo and the deck (for example, with snow, ice, sand, gravel, and oil):
- Use tiedowns attached to the cargo.
- Use a means to improve the friction such as friction mats or tiedown that pass over the cargo.
- Use blocking and tiedowns.
What is the minimum Working Load Limit for the entire securement system?
- 50% of cargo weight.
- 100% of cargo weight.
- 80% of cargo weight.
- 20% of cargo weight.
Note: The minimum WLL requirement for the securement system is 50%. More tiedown capacity should be used if you need to secure an article against any movement.
An intermodal container is:
- A specialized container, primarily used to contain and transport materials in the waste, recycling, construction/demolition, and scrap industries, which are used in conjunction with specialized vehicles, in which the container isloaded and unloaded onto a tilt frame body by an articulating hook-arm.
- A reusable, transportable enclosure that is especially designed with integral locking devices that secure it to a container chassis trailer to facilitate the efficient and bulk shipping and transfer of goods by, or between various modes of transport, such as highway, rail, sea, and air.
- A platform or tray on which cargo is placed so that it can be handled as an article. (Same as "Skid")
- A vehicle especially built and fitted with locking devices for transport.
Intermodal Container:
A reusable, transportable enclosure that is especially designed with integral locking devices that secure it to a container chassis trailer to facilitate the efficient and bulk shipping and transfer of goods by, or between various modes of transport, such as highway, rail, sea, and air.
When a tiedown is attached directly to the cargo, what is the ideal angle where it attached to the vehicle?
- 90 degrees.
- Between 45 and 60 degrees.
- It doesn't matter.
- Less than 45 degrees.
The angle where the tiedown attaches to the vehicle should be shallow, not deep (ideally less than 45).
What is the presumed resistance to horizontal movement of friction mats?
- 0
- 100% of cargo weight.
- 50% of cargo weight.
- 20% of cargo weight.
Note: Friction mats, which are not marked by the manufacturer, are assumed to provide a resistance to horizontal movement equal to 50% of the cargo weight that is resting on the mat.
Complete!
You can Return To The Table Of Contents




 TT On Facebook
TT On Facebook