Note: Your are not logged in. We can not keep your scores or track your progress unless you Register and Log In
Preventing Securement Failure
Use a securement system to immobilize metal coils to ensure they are prevented from sliding, tipping or rolling.
Comply with specific securement methods required in regulations.
Application:
-
NYS-CDL DRIVER LICENSE METAL COIL ENDORSEMENT (âMâ):
Commercial drivers licensed in New York State are required to get the New York State Metal Coil Endorsement in order to transport a metal coil, or a group of metal coils, weighing more than 5,000 lbs (2,268 kg.)
-
ANY COMMERCIAL VEHICLE OR DRIVER:
Drivers licensed in other states, per the FMCSA regulations, are not bound by this New York-specific regulation.
The following securement requirements are for metal coils transported on flatbed vehicles, van-type vehicles or intermodal containers that have anchor points. Securement requirements for sided vehicles or intermodal containers without anchor points are covered at the end of this section.
Securement Requirements for a Single Metal Coil with Eyes Vertical:
If the coil is fastened to a pallet, the pallet must be strong enough so it cannot collapse under the forces described in the performance criteria (Section 1).
Tie-downs must be arranged in the following manner to prevent the coils from tipping in the forward, rearward and side-to-side (lateral) directions:
- At least one indirect tie-down attached diagonally from the left side of the vehicle, across the eye of the coil, to the right side of the vehicle;
- At least one indirect tie-down attached diagonally from the right side of the vehicle, across the eye of the coil, to the left side of the vehicle;
- At least one indirect tie-down attached side-to-side over the eye of the coil;
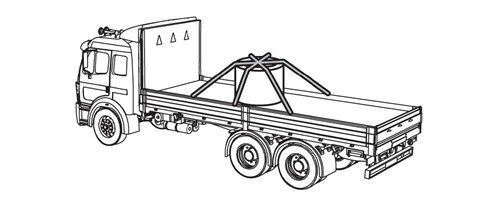
Either blocking and bracing, friction mats or direct tie-downs must be used to prevent forward - rearward movement.
Note: Use a friction mat under the pallet to increase the friction between the pallet and the deck.
The coil should be secured to the pallet to withstand all the forces in the performance criteria (Section 1).
The sum of the working load limits from all tie-downs must be at least 50% of the weight of the coils.
Multiple-Choice Questions:
A single metal coil with eye vertical weighing 6,350 lbs requires tiedowns with a minimum aggregate WLL of:
- 10,000 lbs.
- 6,350 lbs.
- 3,175 lbs
- 12,700 lbs.
The sum of the working load limits from all tiedowns must be at least 50% of the weight of the coils.
CDL drivers from New York State require the Metal Coils Endorsement when transporting metals coils weighing:
- Less than 10,000 lbs.
- More than 2,268 lbs.
- More than 10,000 lbs.
- More than 5,000 lbs.
NYS-CDL DRIVER LICENSE METAL COIL ENDORSEMENT (M):
Commercial drivers licensed in New York State are required to get the New York State Metal Coil Endorsement in order to transport a metal coil, or a group of metal coils, weighing more than 5,000 lbs (2,268 kg.)
When securing a single metal coil with eye vertical, tiedowns must be arranged according the all of the following except:
- At least one indirect tiedown attached diagonally from the left side of the vehicle, across the eye of the coil, to the right side of the vehicle;
- At least one indirect tiedown attached side-to-side over the eye of the coil;
- At least one direct tiedown towards both the front and the rear of the load.
- At least one indirect tiedown attached diagonally from the right side of the vehicle, across the eye of the coil, to the left side of the vehicle;
Tiedowns must be arranged in the following manner to prevent the coils from tipping in the forward, rearward and side-to-side (lateral) directions:
- At least one indirect tiedown attached diagonally from the left side of the vehicle, across the eye of the coil, to the right side of the vehicle;
- At least one indirect tiedown attached diagonally from the right side of the vehicle, across the eye of the coil, to the left side of the vehicle;
- At least one indirect tiedown attached side-to-side over the eye of the coil;
Complete!
You can Return To The Table Of Contents




 TT On Facebook
TT On Facebook